What is the Carrier-to-Noise Ratio (C/N)? How do I analyze it on an RMT spectrum analyzer?
In wireless communications and RF testing, the Carrier-to-Noise Ratio (C/N) is a crucial parameter that directly reflects signal quality. This article will provide a detailed introduction to the basic concepts of C/N and, through practical examples, demonstrate how to accurately analyze it using the TFN brand RMT handheld spectrum analyzer.
What is the Carrier-to-Noise Ratio?
The Definition and Importance of the C/N Ratio
The C/N ratio is the ratio of carrier signal power to noise power, typically expressed in decibels (dB). It is a key indicator of communication system performance. A high C/N ratio indicates clear signals and stable transmission, while a low C/N ratio may lead to signal distortion and increased bit error rates.
In practical applications, the C/N ratio is widely used in satellite communications, broadcast television, mobile networks, and other scenarios, helping engineers quickly determine whether signals are subject to interference and whether the system is operating optimally.
Why choose an RMT handheld spectrum analyzer?
The TFN RMT series handheld spectrum analyzers offer high accuracy, portability, and ease of operation, making them ideal for field testing and on-site maintenance. Their wide frequency range, high-resolution bandwidth, and diverse intelligent measurement functions make them an ideal tool for analyzing carrier-to-noise ratios.
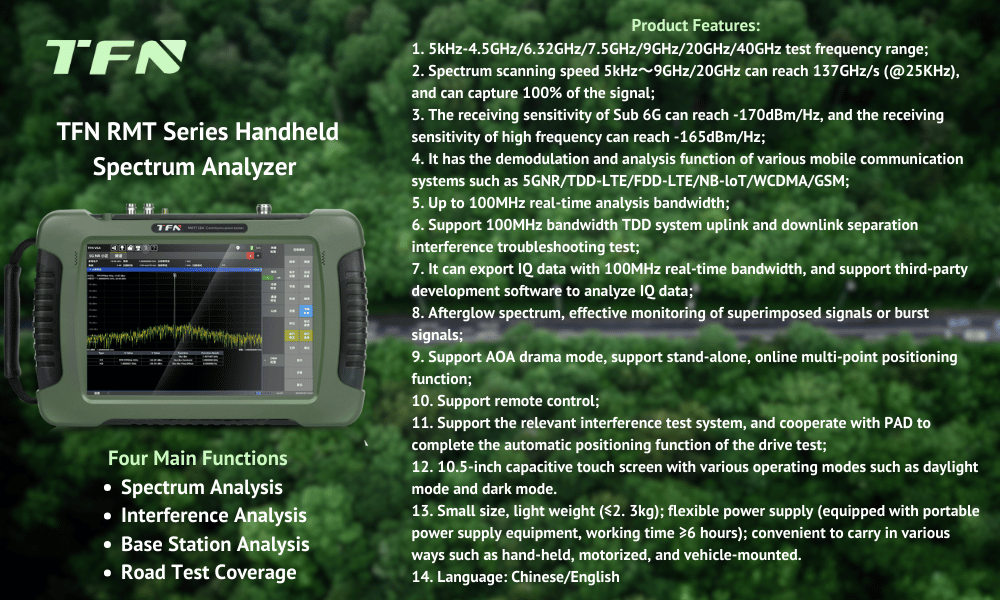
How do I analyze the carrier-to-noise ratio on an RMT spectrum analyzer?
Preparation
Before beginning the test, ensure the following steps have been completed:
1. Connect the signal source to the RF input port of the RMT spectrum analyzer via an RF cable.
2. Turn on the instrument and allow it to warm up for at least 30 minutes to ensure stable measurement results.
3. Set basic parameters such as center frequency, reference level, and resolution bandwidth to match the signal to be measured.
Carrier-to-Noise Ratio Test Steps
The following is the detailed process for measuring the carrier-to-noise ratio using an RMT spectrum analyzer:
1. Enter spectrum analysis mode and select the [Signal-to-Noise Ratio] function in the [Measurement] menu.
2. Set the center frequency to the signal carrier frequency and adjust the reference level based on the signal strength.
3. Use the [Marker] function to locate the carrier peak and record its power value.
4. Move the marker to the frequency where there is no signal and read the noise power value at that frequency.
5. The instrument automatically calculates and displays the ratio of carrier power to noise power, i.e., the carrier-to-noise ratio (C/N).
Precautions
1. Ensure that the input signal does not exceed the instrument's maximum safe input level (+26dBm) to avoid damage.
2. Minimize ambient electromagnetic interference during testing to improve measurement accuracy.
3. Use the [Average] function to take multiple samples to obtain a more stable carrier-to-noise ratio reading.
Conclusion
Carrier-to-noise ratio is a core parameter for evaluating communication signal quality. The TFN RMT handheld spectrum analyzer, with its powerful functionality and portability, provides engineers with an efficient and reliable testing method. Mastering carrier-to-noise ratio measurement methods is crucial for base station maintenance, signal troubleshooting, and educational experiments.
Through the above steps, you can not only quickly complete carrier-to-noise ratio analysis but also gain a deep understanding of the relationship between signal and noise, laying a solid foundation for subsequent system optimization.
